- What is AI for Business?
- 8 Key Ways AI is Being Used in Business Operations
- What are the Challenges of Using AI in Business?
- What are the Benefits of Using Artificial Intelligence?
- The Dangers of the Misuse of AI in Business
- What Are Ethical AI Practices?
- 5 Top AI trends in 2026
- Closing Thoughts
- Frequently Asked Questions
£400 billion. Yes, that’s how much the UK economy can expect to earn from AI innovation by 2030.
If you have been following the UK’s new AI Opportunities Action Plan, you will realise that Britain has a real shot at being an AI powerhouse. To give you an idea of the scale of this project, there are plans to build a supercomputer that can play half a million chess games against itself every second.
The UK is already the third-largest AI market globally, and this Action Plan doesn’t gloss over the challenges. According to the BBC, “This is the first post-Brexit push for innovation and growth which looks credible.”
The Action Plan primarily explores three broad themes:
-
Investing in AI Infrastructure
-
Pushing for AI adoption in the public sector
-
Securing the UK’s future with homegrown AI
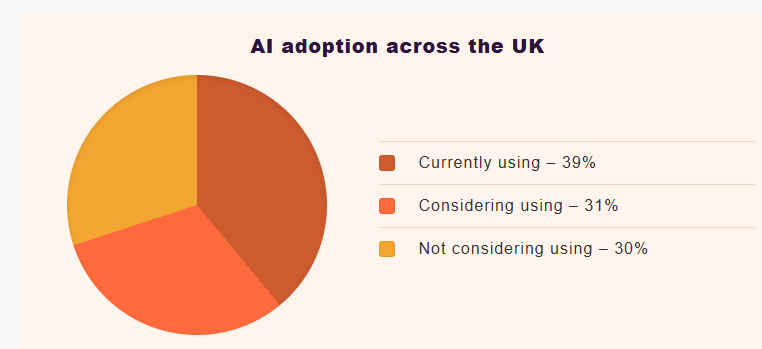
It may help to look at the current state of AI adoption across the UK. This chart breaks down the stages of AI usage in the UK. And, it’s clear that currently AI adoption in the UK is still in a state of transition.
What is AI for Business?
When people discuss AI in business, they tend to make it sound mind-boggling. In reality, it’s simply computer systems that learn from data and assist with activities such as identifying patterns, predicting consequences, and providing answers.
The reason it is important to business is straightforward. You can’t have teams checking millions of records or predicting markets with pen and paper. AI for business can do the heavy lifting fast, and you still decide what to do with that information.
Here’s what it really does for business:
-
AI processes massive data sets in seconds, so you don’t waste time waiting for reports that guide decisions in busy markets.
-
It looks at customer behaviour, then suggests or delivers services that feel personal, enhancing how people perceive your brand.
-
AI takes care of repetitive jobs like reports or data checks, so your team is free to work on tasks that actually grow the business.
-
With accurate forecasting, AI gives managers a clearer picture of sales, supply needs, and risks, which makes planning less stressful.
8 Key Ways AI is Being Used in Business Operations
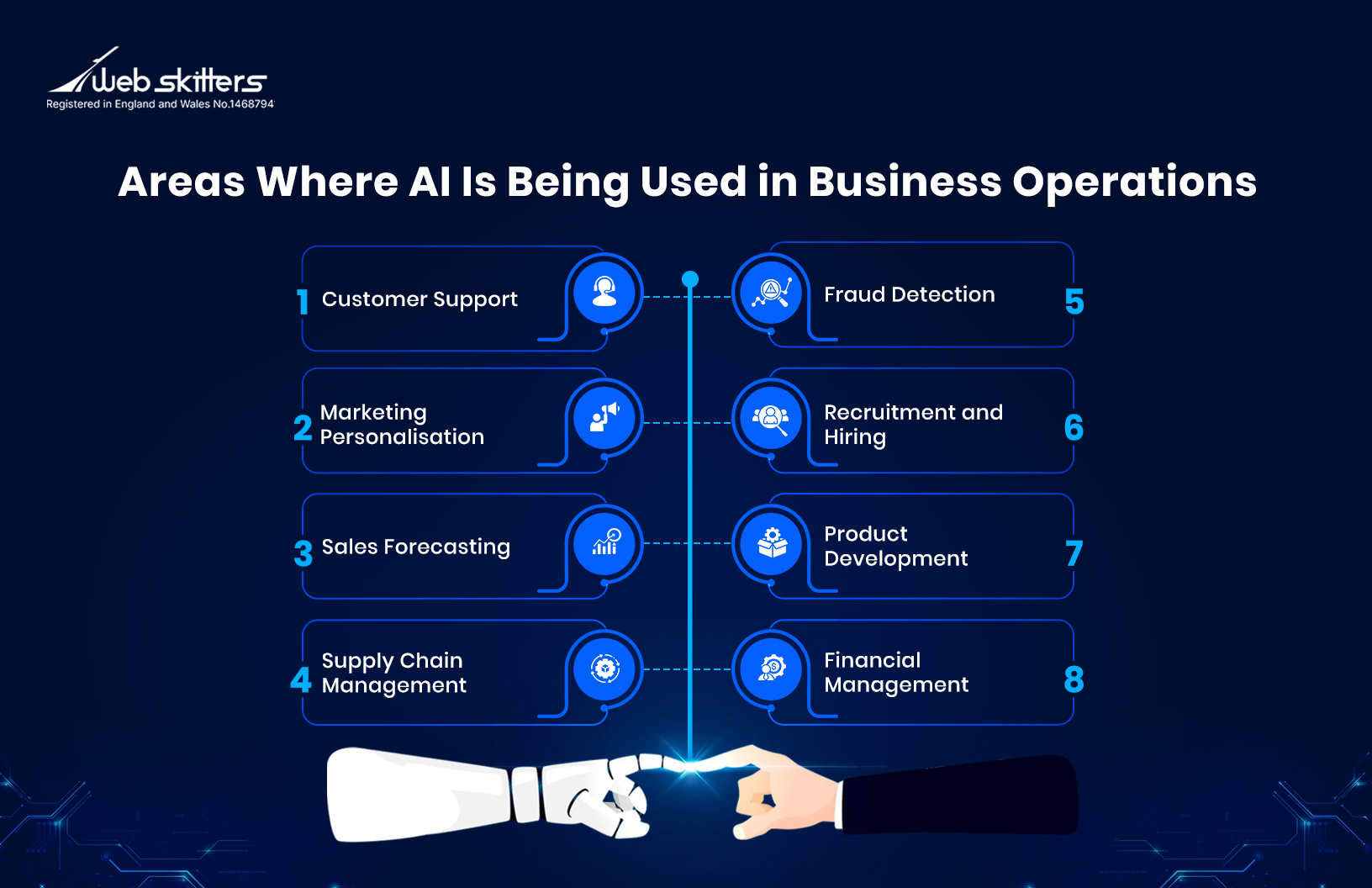
Many still believe that AI exists only in labs or large tech firms. In reality, AI applications for business are already embedded in day-to-day operations. AI for business is no longer in the testing phase. Let’s explore the key AI applications being used right now.
1. Customer Support
Noticed chatbots on websites? They typically answer questions instantly. These are not just simple scripts anymore. AI development services can provide sophisticated systems capable of understanding the intent behind what a customer types, offer personalised answers, and even escalate to a human if the query goes beyond their purview.
It often means fewer frustrated individuals waiting in long lines and less stress for call centre staff. The AI continues to work 24/7, getting smarter with each interaction, so the responses improve over time. Instead of having frustrated customers on your hands, they are more likely to be helped quickly and return.
2. Marketing Personalisation
Remember when marketing used to be a guessing game? You would put ads out and hope they reached the right people. With AI, companies now know who to target and when. AI looks at browsing patterns, previous purchases, and even how long someone spends on a page. From this, it creates campaigns that feel tailor-made.
Ecommerce platforms use AI to recommend products based on what you’ve already bought. This is not random. It’s calculated to make the customer feel understood. Businesses save money because they aren’t wasting ads on people who will never buy. Instead, they are increasing conversion rates with fewer resources.
3. Sales Forecasting
Forecasting sales is difficult without good data. Too often, businesses overstock and lose money or understock and lose customers. AI helps by analysing past sales, seasonal trends, and even external factors like market conditions or weather.
Of course, intuition cannot be replaced. It’s about giving managers a solid data-backed view of what’s likely to happen. When the numbers are more accurate, businesses plan production and inventory better. They also avoid the kind of big financial mistakes that happen when forecasts are just based on gut feeling.
4. Supply Chain Management
The supply chain is complex, and one small delay can ripple through the whole system. AI helps companies track inventory, supplier performance, and transport conditions in real time. If something is about to go wrong, it flags it before the damage is done.
AI systems can reroute shipments if there’s a sudden disruption like bad weather or political issues. They can also identify which suppliers are most reliable, so businesses reduce risk over the long term. This gives companies an edge because they can adapt quickly instead of getting stuck with problems they didn’t see coming.
5. Fraud Detection
Fraud is one of the largest threats to banks, ecommerce, and online payment. Old systems used fixed rules, but fraudsters always had a way around them. AI operates in a different way. It processes thousands of transactions in an instant, searching for unusual patterns.
If a transaction appears suspicious (e.g., an unexpected buy in another country) it is flagged in seconds. The system adapts to each case, so it becomes increasingly difficult for the fraudsters to keep one step ahead. This safeguards both the business and the customer, making the platform even more trusted.
6. Recruitment and Hiring
Recruitment is always sluggish and biased. AI accelerates the process by reviewing CVs and applications to point out the most suitable candidates. No one is claiming it substitutes human judgment during interviews, but it shortens the time spent by HR teams sorting through hundreds of applications.
Anonymisation of candidate information also occurs in some systems to minimise unconscious bias at an early screening stage. This allows a more equitable and streamlined process within companies. You are able to make hires quicker, and have a greater chance of getting the right person for the job.
7. Product Development
Developing new products takes time, money, and risk. AI helps companies cut down all three. It can analyse customer feedback, market trends, and competitor activity to predict what features will be popular. Instead of guessing, businesses build products that already have demand.
Developers who need to simulate designs or run virtual tests before building prototypes can depend on AI system to handle these tasks with ease. You save a considerable amount as fewer physical samples are required, and it minimises the risk of failure. The result is speedy innovation cycles and an increased probability of success once the product is in the market.
8. Financial Management
Finance departments deal with endless data in areas like spending, budgets, risks, and compliance. AI makes this workload easier by monitoring accounts in real time. It can spot unusual spending, predict cash flow shortages, and suggest where money is being wasted.
This information is invaluable to managers. They are not forced to wait until the end of the quarter to detect where problems are. AI systems allow you to be proactive, prevent losses, and keep finances stable. The best part is that your investors and stakeholders also gain more confidence when they notice that your company is using reliable tools to manage its money.
What are the Challenges of Using AI in Business?
Artificial intelligence may seem like the magic pill that will solve all your business issues. But, as any AI agency in London will tell you, the reality is not always that rosy. There are genuine challenges that need to be addressed when introducing AI in business workflows.
1. High Adoption Costs
The initial implementation costs of AI are certainly not cheap. You may need sophisticated software and robust hardware, to say nothing of the personnel training expenses. So, yes, the costs can compound quickly. Most small businesses are afraid to take the plunge because the initial investment is daunting. Consider it, would you put your budget at risk on something you don’t know will provide instant results?
2. Shortage of Qualified Talent
Only professionals trained to use AI can be trusted to wield it to its full potential. Unfortunately, those people are not always easy to find. Data scientists, AI engineers, and analysts are in high demand. In case you’re wondering why salaries for these roles are so high, it’s because there just aren’t enough trained professionals to meet the growing need.
3. Data Privacy and Security Concerns
Without valuable data, AI cannot function. So, the more data it receives, the more intelligent it becomes. With data comes responsibility, though. Companies must be very careful how they gather, store, and use customer data. It’s easy to see how one breach of security could topple trust built up over years.
4. Integration with Existing Systems
Firms tend to already have systems and software operating their businesses. Inserting AI into those configurations is not always easy. It sounds peculiar, but some firms literally disrupt workflows when they attempt to “upgrade” without planning. That would be a wise decision, since smooth integration requires strategy, not technology alone.
5. Ethical and Bias Issues
The fact is that AI is only as unbiased as the information it’s trained on. Say the information has underlying biases. What will happen is that the AI may render unfair or deceptive decisions. Suppose AI is being used for the hiring process of a company, and it inadvertently screens out certain groups. That would be a terrifying prospect indeed. Since reputation means everything in business, these errors could damage it irreparably.
The right AI development services from a reputable agency can solve these issues at the root.
What are the Benefits of Using Artificial Intelligence?
You already know the challenges of AI in business. But, where is it that AI truly shows its strength, with hard data behind real business gains? Let’s see.
1. Accelerated Decision-Making and Productivity
Generative AI helps teams quickly surface answers from vast internal libraries by understanding natural language queries. This speeds decision-making in ways that were not possible before.
Your business can make highly informed decisions without searching through scores of documents manually.
This way, your analysts can focus on interpreting insights, rather than looking for them.
Furthermore, SMEs (small and medium enterprises) in the UK that are using AI tools could achieve between 27 and 133% productivity gains, according to research conducted by St Andrews Business School.
2. Real Economic Value and Revenue Expansion
McKinsey & Company research shows firms using AI to reshape their business models are 1.5 times more likely to achieve significant revenue growth. Think about it this way, AI is not being adopted merely for smart operations; it is helping to open new markets and services.
Contrary to popular belief, AI is not only about automation. A clear case in point is the ArteraAI Prostate Biopsy Assay. It is an AI tool that’s currently being used in NHS hospitals to analyse digitised images of patient biopsies. The AI tool is designed to aid doctors in treating prostate cancer.
This kind of breakthrough is possible when AI is built in from the start and not as an afterthought.
3. Democratised Access and Broader Adoption
AI tools are no longer the preserve of Silicon Valley giants. McKinsey notes that modern AI is easier to implement, and 21% of surveyed firms have redesigned their workflows to include generative AI.
Plus, the aim of the Action Plan is that there is AI is widely embraced across the UK, including SMEs, universities, and underserved populations. They expect to ‘level the playing field for innovation’ as it were and continue making inroads in terms of AI literacy.
4. Autonomous “AI Agents” Supporting Work
Globally renowned McKinsey and Company have internally deployed 12,000 AI agents to handle tasks like research summaries and logic checks LinkedIn. That’s not science-fiction, these agents support consultants around the clock.
What’s good about these agents is that they run independently within defined boundaries. They reduce the possibility of errors and speed up workflows without replacing human roles. This way, your organisation would be able to scale up efficiently without needing to hire more employees.
5. Massive Economic Opportunity Worldwide
AI’s boost to global GDP could be up to 15 percentage points by 2035, according to PwC’s Value in Motion report, which is on par with the growth jump that came from 19th-century industrialisation.
It’s fair to say that’s a seismic shift.
Industries like retail, banking, or pharma stand to gain billions each year. When you consider the scale, it’s obvious that businesses that adapt first will be in the lead.
6. Rich Customer Experience and Reduced Complexity
You may not have realised it, but half of the customer interactions in sectors like banking and telecom are already handled by machines. Generative AI could cut human-serviced contacts by another 50% and improve resolution times by 9%, while boosting satisfaction and lowering escalations by 25%.
Customer support becomes faster, extremely precise, and proportional to volume. Employees are able to focus solely on the most challenging cases, rather than the routine ones. This way customers receive will answers without delay or repeating questions.
Unfortunately there is quite a lot of scope for the misuse of AI, which can be detrimental to both individuals and businesses alike. We’ll go through some of the scenarios you should avoid.
The Dangers of the Misuse of AI in Business
One of the glaring problems is that the misuse of AI can undo any gains that businesses may leverage from it. Misuse can come in many forms, including bias, cybersecurity breaches, non-consensual data collection and much more. Let’s look at some in more detail.
Biased and unfair decisions
Training data might contain human biases which can then impact the ML (machine learning) algorithms. This in turn can lead to lopsided outcomes which can include gender bias, bias against certain races and ethnic groups. If that’s the case, AI is likely to reproduce and scale those errors across recruitment, money lending, pricing and other areas.
Breach of Intellectual Property
Right now there’s a lot of ambiguity around who AI content and IP issues. There’s two levels at which this can happen. One is at the training phase, where the AI model trains on copyrighted works. The other is the creation phase, where the AI content generated is substantially similar to existing copyrighted material.
Security and shadow use
Shadow AI is simply the use of AI tools that have not been approved by an organisation. Unfortunately, 71% of UK employees are using such tools. Because of these tactics, the potential for sensitive company or client data getting leaked is high.
Overpromising and project failure
Have you heard of ‘AI washing’? It’s when businesses make exaggerated claims about the AI capabilities of their services and/or products. These unsubstantiated claims mislead consumers and results in disappointment and loss of trust when the product fails to meet the promised outcome.
What Are Ethical AI Practices?
As can be expected with any rapidly growing technology, it is understandable the AI too comes with its fair share of ethical concerns. This is why it is a paramount that you know what ethical AI practices are and why they matter.
So, if you plan on using AI for your business, it’s best if you incorporate ethical AI practices from the very start. They include:
Fairness and non-discrimination
The AI algorithms you use should be trained to be free of bias. This will ensure equitable outcomes and steer clear of any discrimination against individuals or groups.
Transparency and explainability
It’s important to be transparent about how your AI model arrives at decisions. Users should be told when they are interacting with an AI (like a chatbot), and the reasoning behind the AI’s conclusions should be explainable.
Privacy and data protection
The underlying priority of your AI system should be to safeguard user privacy and adhere to data protection regulations.
Accountability
When building an AI system there must be clear governance structures and mechanisms for identifying and rectifying errors. Organizations would be held accountable for the outcomes of their AI systems.
Human oversight and agency
The main goal of including human oversight in AI systems is to ensure that no decision remains unchecked. In this case, human agents will have the final say in important decisions, even in instances where AI is used to inform those choices.
Safety and security
AI systems must be protected from attacks and designed to avoid safety risks. This includes all phases, from training data to system outputs and even implementing measures such as user access controls and adversarial training (protocol to train AI to defend itself against various attacks).
Environmental and societal well-being
Since AI was created for the advancement of individuals, society, and the environment, it’s easy to see why AI systems need to be evaluated for its impact on them. This involves the incorporating sustainability into its design and implementation.
While keeping ethical considerations in mind, UK businesses that are aiming to increase AI adoption need to be aware of the current cutting-edge trends in the realm of AI.
5 Top AI trends in 2026
At present and in the coming future, AI will continue to be a transformative force. Companies across the globe will reshape their business models and rethink their operations, that is, if they expect to stay competitive.
1. Multimodal AI
Systems with multimodal AI can process and understand in a range of different formats, be it text, audio, images and video. How it works is when information arrives from different formats, it has enough context. With this context it comes to decisions that feel closer to how people naturally understand things.
2. Agentic AI
Remember the movie ‘The Matrix’? Well, Agentic AI is similar, without the whole AI becoming sentient part.
It’s designed in such a way that instead of waiting for someone to constantly instruct it to perform a specific task, the system learns how to take the next step independent of human intervention.
3. Artificial Neural Networks
Have you ever noticed how humans start spotting patterns automatically after enough exposure to something? Neural networks work in a similar direction. The model can learn gradually, then improving the accuracy of what it predicts over time. And, as you can imagine it has several real-world applications whether it’s facial recognition, fraud detection, forecasting and so on.
4. AI-powered Cybersecurity
The problem with cybersecurity threats is that they tend to escalate far quicker than people can manually track. AI cybersecurity tools can isolate signals by analyzing massive datasets. They are trained to proactively respond to anomalies and prevent any attempts of an attack.
5. Edge AI
Ordinarily, data is sent to the cloud, processed there and returned. Edge AI removes that dependency by running the intelligence right at the data source (locally). This is exactly why edge AI is used in critical real-time environments like hospitals, traffic management, defect detection etc.
Closing Thoughts
It’s clear by now that AI adoption in the UK is not just a vision. The AI Opportunities Action Plan is backed by real numbers, infrastructure plans, and global ambition.
Britain is actively positioning itself among the world’s AI powerhouses.
If you are looking for a good AI agency in London, Webskitters Ltd is your best bet.
Trusted since 2010, we develop award-winning web, app, and AI-powered solutions, with a UK-based team and a proven global track record that sets them apart from the rest.
Let us help you get started with your AI journey.
Frequently Asked Questions
1. Why is the UK investing so heavily in AI now?
The government wants the UK to be competitive globally, and AI is where future economic growth will come from. Britain does not want to fall behind other major tech nations.
2. Will AI replace workers completely in the UK?
No. AI mostly automates routine tasks, while people remain needed for judgment, empathy, negotiation, creativity, and strategy. The aim is to increase productivity, not remove entire departments overnight.
3. How soon can small UK businesses realistically benefit from AI?
Small businesses can start benefiting right now through widely available tools that improve marketing, sales, and customer support. You do not need expensive custom systems to begin.
4. Should UK businesses be worried about ethical and legal risks?
Yes, UK businesses need strong controls around fairness, privacy, and accountability. If these are ignored, the regulator pressure will rise and public trust will drop very quickly.
5) Is AI difficult to integrate into existing systems?
It depends on planning. Integration becomes smoother when there is a clear business goal, good data hygiene. Plus, you would require a phased approach to avoid abrupt changes in one go.

